MATLAB PARALLEL SERVER ON THE SCC
This document provides the steps to configure MATLAB to submit jobs to a cluster, retrieve results, and debug errors. The procedure in here only applies to MPG users. University of Göttingen users have NO access to the MATLAB Parallel Server.
Warning
INSTALLATION and CONFIGURATION – MATLAB client on the desktop
The SCC MATLAB support package can be found at here. Download the appropriate archive file and start MATLAB. The archive file should be untarred/unzipped in the location returned by calling
>> userpathConfigure MATLAB to run parallel jobs on your cluster by calling configCluster. configCluster only needs to be called once per version of MATLAB.
>> % Create new HPC profile
>> configCluster
Username on SCC (e.g. jdoe): USER-ID
Must set WallTime before submitting jobs to SCC. E.g.
>> c = parcluster;
>> % 5 hour, 30 minute walltime
>> c.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = '05:30:00';
>> c.saveProfile
NOTICE: Connecting to SCC requires an SSH keypair.
You will be prompted for your private key upon
submitting your first job.
Complete. Default cluster profile set to "SCC R2022b"
>>Jobs will now default to the cluster rather than submit to the local machine.
Note
If you would like to submit to the local machine instead then run the following command:
>> % Get a handle to the local resources
>> c = parcluster('local');CONFIGURING JOBS
Prior to submitting the job, we can specify various parameters to pass to our jobs, such as queue, e-mail, walltime, etc. The following is a partial list of parameters. See “AdditionalProperties” for the complete list. None of these are required.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster('SCC R2022b');
Must set WallTime before submitting jobs to SCC. E.g.
>> c = parcluster;
>> % 5 hour, 30 minute walltime
>> c.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = '05:30:00';
>> c.saveProfile
NOTICE: Connecting to SCC requires an SSH keypair.
You will be prompted for your private key upon
submitting your first job.
Complete cluster profile setup.
Input path to $HOME on SCC (e.g. /user/first.last/u#####): /user/damian/pietrus/u12352
Configuration complete.
>> % Specify the wall time (e.g., 5 hours)
>> c.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = '05:00:00';
>> c.AdditionalProperties.Partition = 'medium';
>> c.saveProfileSave changes after modifying “AdditionalProperties” for the above changes to persist between MATLAB sessions.
>> c.saveProfileTo see the values of the current configuration options, display “AdditionalProperties”.
>> % To view current properties
>> c.AdditionalPropertiesUnset a value when no longer needed.
>> % Turn off email notifications
>> c.AdditionalProperties.EmailAddress = '';
>> c.saveProfileThe created profile can be found on the MATLAB Client:
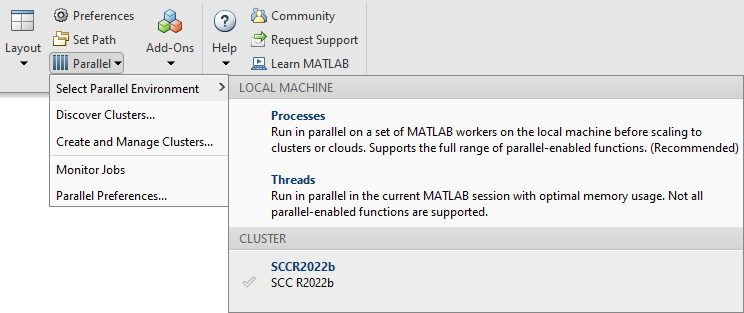
INTERACTIVE JOBS - MATLAB client on the cluster
To run an interactive pool job on the cluster, continue to use “parpool” as you’ve done before.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster;
>> % Open a pool of 64 workers on the cluster
>> pool = c.parpool(64);Rather than running local on the local machine, the pool can now run across multiple nodes on the cluster.
>> % Run a parfor over 1000 iterations
>> parfor idx = 1:1000
a(idx) = …
endOnce we’re done with the pool, delete it.
>> % Delete the pool
>> pool.deleteINDEPENDENT BATCH JOB
Use the batch command to submit asynchronous jobs to the cluster. The batch command will return a job object which is used to access the output of the submitted job. See the MATLAB documentation for more help on batch.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster("SCC R2022b");
>> % Submit job to query where MATLAB is running on the cluster
>> job = c.batch(@pwd, 1, {}, 'CurrentFolder','.');
>> % Query job for state
>> job.State
>> % If state is finished, fetch the results
>> job.fetchOutputs{:}
>> % Delete the job after results are no longer needed
>> job.deleteNote
In case this is the FIRST time you submit a job to the cluster the following window will appear to select the SSH key file for the connection:
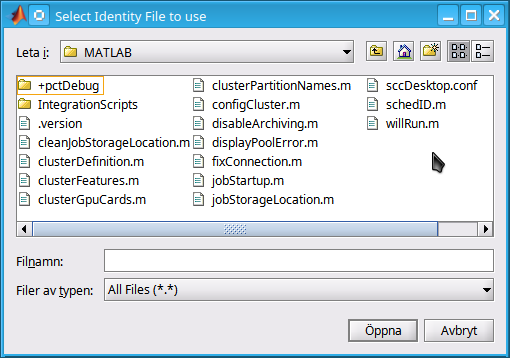
To retrieve a list of currently running or completed jobs, call “parcluster” to retrieve the cluster object. The cluster object stores an array of jobs that were run, are running, or are queued to run. This allows us to fetch the results of completed jobs. Retrieve and view the list of jobs as shown below.
>> c = parcluster;
>> jobs = c.Jobs;Once we’ve identified the job we want, we can retrieve the results as we’ve done previously. “fetchOutputs” is used to retrieve function output arguments; if calling batch with a script, use load instead. Data that has been written to files on the cluster needs be retrieved directly from the file system (e.g. via ftp). To view results of a previously completed job:
>> % Get a handle to the job with ID 2
>> job2 = c.Jobs(2);Note
You can view a list of your jobs, as well as their IDs, using the above c.Jobs command.
>> % Fetch results for job with ID 2
>> job2.fetchOutputs{:}PARALLEL BATCH JOB
Users can also submit parallel workflows with the batch command. Let’s use the following example for a parallel job, which is saved as “parallel_example.m”.
function [t, A] = parallel_example(iter)
if nargin==0
iter = 8;
end
disp('Start sim')
t0 = tic;
parfor idx = 1:iter
A(idx) = idx;
pause(2)
idx
end
t = toc(t0);
disp('Sim completed')
save RESULTS A
endThis time when we use the batch command, to run a parallel job, we’ll also specify a MATLAB Pool.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster;
>> % Submit a batch pool job using 4 workers for 16 simulations
>> job = c.batch(@parallel_example, 1, {16}, 'Pool',4, ...
'CurrentFolder','.');
>> % View current job status
>> job.State
>> % Fetch the results after a finished state is retrieved
>> job.fetchOutputs{:}
ans =
8.8872The job ran in 8.89 seconds using four workers. Note that these jobs will always request N+1 CPU cores, since one worker is required to manage the batch job and pool of workers. For example, a job that needs eight workers will consume nine CPU cores.
We’ll run the same simulation but increase the Pool size. This time, to retrieve the results later, we’ll keep track of the job ID.
Note
For some applications, there will be a diminishing return when allocating too many workers, as the overhead may exceed computation time.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster;
>> % Submit a batch pool job using 8 workers for 16 simulations
>> job = c.batch(@parallel_example, 1, {16}, 'Pool', 8, ...
'CurrentFolder','.');
>> % Get the job ID
>> id = job.ID
id =
4
>> % Clear job from workspace (as though we quit MATLAB)
>> clear jobOnce we have a handle to the cluster, we’ll call the “findJob” method to search for the job with the specified job ID.
>> % Get a handle to the cluster
>> c = parcluster;
>> % Find the old job
>> job = c.findJob('ID', 4);
>> % Retrieve the state of the job
>> job.State
ans =
finished
>> % Fetch the results
>> job.fetchOutputs{:};
ans =
4.7270The job now runs in 4.73 seconds using eight workers. Run code with different number of workers to determine the ideal number to use. Alternatively, to retrieve job results via a graphical user interface, use the Job Monitor (Parallel > Monitor Jobs).
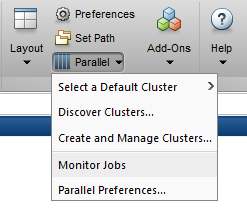
DEBUGGING
If a serial job produces an error, call the “getDebugLog” method to view the error log file. When submitting independent jobs, with multiple tasks, specify the task number.
>> c.getDebugLog(job.Tasks(3))For Pool jobs, only specify the job object.
>> c.getDebugLog(job)When troubleshooting a job, the cluster admin may request the scheduler ID of the job. This can be derived by calling schedID
>> schedID(job)
ans =
25539HELPER FUNCTIONS
| Function | Description | Desktop-only |
|---|---|---|
| clusterFeatures | List of scheduler features/constraints | |
| clusterGpuCards | List of cluster GPU cards | |
| clusterQueueNames | List of scheduler queue names | |
| disableArchiving | Modify file archiving to resolve file mirroring issue | true |
| fixConnection | Reestablish cluster connection | true |
| willRun | Explain, why job is not running |
TO LEARN MORE
To learn more about the MATLAB Parallel Computing Toolbox, check out these resources: